Yes, a bad turbo can cause low oil pressure. A failing turbo can leak oil, reducing overall engine oil pressure.
Turbochargers play a crucial role in boosting engine performance by forcing extra air into the combustion chamber. A faulty turbocharger not only hampers engine efficiency but can also lead to significant mechanical issues. One common problem is a drop in oil pressure, which occurs when the turbo leaks oil.
This leakage reduces the amount of oil available to maintain proper pressure throughout the engine. Low oil pressure can result in inadequate lubrication, leading to increased engine wear and potential damage.
Regular maintenance and timely inspections can help prevent turbocharger failures, ensuring your engine remains in optimal condition.
Introduction To Turbocharged Engines
Turbocharged engines are popular in modern cars. They offer more power and efficiency. A turbocharger compresses air entering the engine. This process allows more fuel to burn and increases power output.
Turbocharged engines have components working together. These include the turbo, oil system, and various sensors. Understanding these parts is key to diagnosing engine issues. One common problem is low oil pressure.
The Role Of Turbos
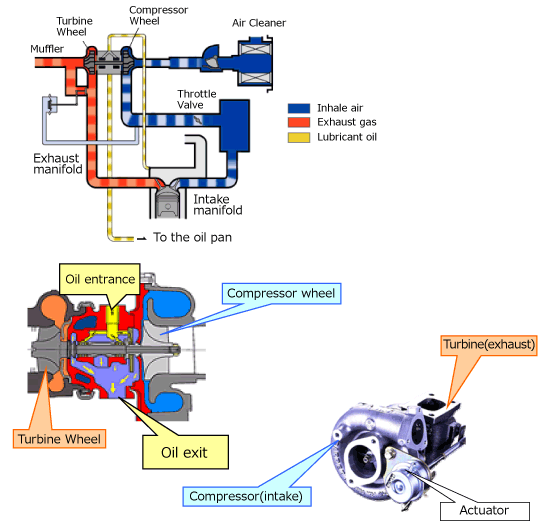
The turbocharger plays a vital role in your engine. It uses exhaust gases to spin a turbine. This turbine compresses air and forces it into the engine. More air means more power.
But turbos also need oil. Oil lubricates the moving parts inside the turbo. It keeps the turbo running smoothly. If the turbo fails, it can affect the whole engine.
Basics Of Oil Pressure
Oil pressure is crucial for engine health. It ensures oil reaches all engine parts. Low oil pressure can cause serious damage.
Oil pressure depends on the oil pump and the condition of the oil. It also relies on the engine’s design and health. A bad turbo can leak oil. This can lower the oil pressure and harm the engine.
Regular maintenance helps avoid these issues. Check your oil levels and turbo health often. Keep your engine running smoothly and efficiently.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Turbocharger | Compresses air for more power |
| Oil System | Lubricates engine parts |
| Oil Pressure | Keeps oil flowing to engine parts |

Credit: www.yourmechanic.com
Symptoms Of Low Oil Pressure
Low oil pressure can lead to serious engine problems. Recognizing the symptoms early can save you from costly repairs. Here are some common signs that your car might be experiencing low oil pressure.
Warning Signs
- Oil Warning Light: The oil warning light on your dashboard is the most obvious sign. If it lights up, it means your oil pressure is low.
- Engine Noise: Unusual noises such as knocking or clattering can indicate low oil pressure. These sounds mean parts of the engine aren’t getting enough lubrication.
- Decreased Engine Performance: You might notice your engine isn’t performing as well as usual. This can be a sign of low oil pressure affecting engine efficiency.
- Burning Oil Smell: A burning oil smell means oil might be leaking or burning due to low pressure. This is a serious issue that needs immediate attention.
- Oil Leaks: Finding oil spots under your car can indicate a leak. This can cause a drop in oil pressure.
Potential Engine Damage
Low oil pressure can cause severe damage to your engine. Here are the potential damages:
| Damage Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Engine Overheating | Low oil pressure means less lubrication. This leads to friction and overheating. |
| Worn-out Bearings | Bearings need oil to function smoothly. Without enough oil, they wear out quickly. |
| Piston Damage | Pistons can seize or get damaged due to insufficient lubrication. |
| Crankshaft Issues | The crankshaft can get damaged due to lack of oil, leading to costly repairs. |
Recognizing these symptoms early can help prevent extensive engine damage. Regular maintenance and oil checks are crucial.
Turbochargers And Oil Pressure: The Connection
Turbochargers play a vital role in enhancing engine performance. But did you know that they also impact oil pressure? Understanding the link between turbochargers and oil pressure can help maintain your vehicle’s health. Let’s dive into how turbos affect oil circulation and why turbo wear can lead to low oil pressure.
How Turbos Affect Oil Circulation
Turbos need oil to stay cool and lubricated. The engine sends oil to the turbo through specific oil lines. This oil helps in reducing friction and heat.
- Oil Flow: Oil flows from the engine to the turbo and back.
- Cooling Effect: The oil keeps the turbo cool, preventing overheating.
- Lubrication: Proper lubrication reduces wear and tear on turbo components.
If the oil doesn’t circulate properly, the turbo can overheat. This can cause serious engine issues.
Turbo Wear And Oil Pressure
Worn turbos can lead to low oil pressure. Let’s look at why this happens.
| Issue | Effect on Oil Pressure |
|---|---|
| Worn Bearings | Can cause oil leaks, reducing overall oil pressure. |
| Oil Line Blockages | Restricted oil flow leads to lower oil pressure. |
| Oil Contamination | Dirty oil can clog lines, affecting oil pressure. |
Worn bearings in the turbo can create gaps. This allows oil to escape, causing leaks and reduced pressure. Blocked oil lines prevent oil from reaching the turbo effectively.
Dirty or contaminated oil can also clog oil lines. This further affects oil pressure and turbo performance.

Credit: www.machinerylubrication.com
Common Causes Of Turbo Failure
Turbochargers are vital for engine performance. They boost power and efficiency. But they can fail. Understanding the causes helps in preventing issues.
Oil Contamination
Oil contamination is a major cause of turbo failure. Dirty oil damages the turbo. It affects the moving parts inside. Contaminants can include dirt, debris, and metal particles.
Contaminated oil leads to increased wear and tear. This reduces the life of the turbocharger. Regular oil changes help avoid this issue.
Inadequate Lubrication
Inadequate lubrication is another common cause. Turbos need a steady oil supply. It keeps the parts moving smoothly. Lack of oil causes friction and heat.
Friction and heat can seize the turbo. This leads to expensive repairs or replacements. Always check the oil level and quality.
Diagnosing The Root Cause
Understanding whether a bad turbo can cause low oil pressure is crucial. Diagnosing the root cause involves detailed inspections and professional diagnosis methods. Ensuring accurate identification helps in effective repairs and maintenance.
Inspection Techniques
Visual inspection is a primary step. Check for oil leaks around the turbocharger. Examine the oil lines for blockages or damage.
Listen for unusual noises. A bad turbo often makes whining or grinding sounds. These noises indicate internal damage.
Check the oil level. Ensure it is at the recommended level. Low oil levels can cause low oil pressure.
| Inspection Area | What to Look For |
|---|---|
| Oil Leaks | Check around turbocharger |
| Oil Lines | Look for blockages or damage |
| Noises | Listen for whining or grinding sounds |
| Oil Level | Ensure it’s at the recommended level |
Professional Diagnosis Methods
Oil pressure tests are essential. Professionals use oil pressure gauges to measure the pressure accurately. Low readings confirm low oil pressure.
Diagnostic scanners help. These devices read error codes from the engine’s computer. Codes related to the turbocharger can indicate issues.
Turbocharger testing involves removing and inspecting the turbo. Experts check for wear and tear and internal damage.
- Use oil pressure gauges for accurate readings.
- Read error codes with diagnostic scanners.
- Inspect the turbocharger for internal damage.
Engine oil analysis can also help. Lab tests reveal oil contamination or degradation. Contaminated oil can affect pressure.
Combining these methods ensures a comprehensive diagnosis. It helps pinpoint whether the turbo is causing low oil pressure.
Impact Of A Failing Turbo On Engine Health
A failing turbo can have serious effects on your engine’s health. It can cause low oil pressure and other issues. Understanding these impacts can help you take action quickly.
Immediate Risks
One of the immediate risks of a failing turbo is low oil pressure. This happens because a damaged turbo can cause oil leaks. The engine relies on proper oil pressure to stay lubricated. Without enough oil, moving parts can wear out quickly.
- Increased friction: Parts rub against each other.
- Heat build-up: Lack of oil causes overheating.
- Component damage: Metal parts can get damaged.
These issues can lead to sudden engine failure. You might notice warning lights on your dashboard. If you see these signs, it’s important to address the problem immediately.
Long-term Consequences
The long-term consequences of a failing turbo are severe. Over time, low oil pressure can cause extensive engine damage. Here are some problems you might face:
- Worn Bearings: Bearings need oil to reduce friction. Without oil, they wear out.
- Engine Seizure: Lack of lubrication can cause the engine to seize up completely.
- Costly Repairs: Fixing these issues can be very expensive.
Below is a table summarizing the immediate and long-term impacts:
| Impact | Immediate | Long-Term |
|---|---|---|
| Friction | Increased | Severe component wear |
| Heat | Build-up | Overheating |
| Damage | Component damage | Engine seizure |
Addressing a failing turbo promptly can prevent these severe outcomes. Ensure regular maintenance to keep your engine healthy.
Repairing A Bad Turbo
Experiencing low oil pressure in your vehicle can be alarming. One potential culprit could be a bad turbo. Addressing this issue promptly is crucial to avoid further engine damage. This section delves into the steps for repairing a bad turbo, guiding you through the decision-making process and cost considerations.
Replacement Vs. Repair
Determining whether to replace or repair your turbo depends on its condition. A minor issue like a worn-out seal might only need a quick fix. Extensive damage, such as a cracked housing, often necessitates a full replacement.
- Minor Issues: Worn-out seals, clogged oil passages, or minor cracks.
- Major Issues: Cracked housing, damaged turbine blades, or significant oil leaks.
Assessing the severity of the problem helps you decide the best course of action. A mechanic can inspect the turbo and provide recommendations.
Cost Considerations
Repairing a turbo can be more cost-effective than replacing it, depending on the damage. Below is a comparison table to help understand potential costs:
| Type of Service | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Minor Repairs | $100 – $300 |
| Major Repairs | $400 – $800 |
| Full Replacement | $1,000 – $3,000 |
Labor costs vary based on your location and the complexity of the job. Obtaining multiple quotes can help you find the best price.
Deciding between replacement and repair involves balancing cost and longevity. Repaired turbos might not last as long as new ones but can save money in the short term. New turbos offer better performance and longer life but come at a higher price.
Preventative Measures For Turbocharged Engines
A failing turbo can indeed cause low oil pressure in turbocharged engines. Regular maintenance and timely inspections help prevent such issues. Ensuring proper lubrication and addressing any signs of wear can keep your engine running smoothly.
Turbocharged engines provide extra power. They also need extra care. Preventative measures ensure your engine runs smoothly and avoids issues like low oil pressure caused by a bad turbo.
Regular Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance keeps your turbocharged engine healthy. Follow these tips:
- Change the oil and filter every 3,000 to 5,000 miles.
- Use high-quality synthetic oil.
- Inspect the turbo for leaks and damage.
- Keep the air filter clean and replace it regularly.
- Ensure the cooling system is functioning properly.
Regular oil changes are crucial. Dirty oil can damage your turbo. High-quality synthetic oil helps your engine run smoothly. Inspecting the turbo for leaks can prevent bigger problems. A clean air filter ensures optimal airflow, and a working cooling system prevents overheating.
Monitoring Oil Health
Monitoring oil health is essential. It helps detect issues early. Use these methods:
- Check oil levels regularly.
- Look for signs of oil contamination.
- Monitor oil pressure gauge.
- Use an oil analysis kit.
Checking oil levels ensures your engine has enough oil. Oil contamination can indicate a problem. Oil pressure gauges help you monitor pressure in real-time. Oil analysis kits can provide detailed information about your oil’s condition.
| Maintenance Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Change Oil | Every 3,000-5,000 miles |
| Inspect Turbo | Every 10,000 miles |
| Replace Air Filter | Every 15,000 miles |
| Check Cooling System | Every 30,000 miles |
Following these guidelines helps maintain your turbocharged engine. Prevent low oil pressure and other issues with regular care. Keep your vehicle running smoothly and efficiently. “`
Case Studies And Real-life Scenarios
Understanding the impact of a bad turbo on oil pressure can be challenging. Real-life experiences and case studies provide valuable insights. These examples highlight how a faulty turbo can lead to low oil pressure.
Successful Repairs
In many cases, identifying a bad turbo early can save the engine. One car owner noticed a sudden drop in oil pressure. After checking, they found the turbo was leaking oil. Replacing the turbo solved the issue. The oil pressure returned to normal levels. The engine was saved from further damage.
Another case involved a truck with low oil pressure warnings. Mechanics discovered the turbo’s oil seals were worn out. They replaced the seals and the oil pressure stabilized. The truck continued to run smoothly.
Avoiding Engine Catastrophe
Ignoring signs of a bad turbo can lead to severe engine damage. One driver ignored low oil pressure warnings for weeks. Eventually, the engine seized up. The repair costs were significant. This scenario emphasizes the importance of timely turbo maintenance.
In another instance, a mechanic found metal shavings in the oil filter. The source was a failing turbo. Replacing the turbo prevented a potential engine failure. Regular oil checks and prompt actions are crucial.
| Scenario | Issue | Solution | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Car | Leaking turbo | Turbo replacement | Normal oil pressure |
| Truck | Worn turbo seals | Seal replacement | Stabilized oil pressure |
| Ignored Warnings | Low oil pressure | No action | Engine seized |
| Metal Shavings | Failing turbo | Turbo replacement | Engine saved |
Regular checks and prompt repairs can prevent major engine issues. A bad turbo can cause low oil pressure. Addressing the problem early ensures the engine’s longevity.
Conclusion: Protecting Your Turbocharged Engine
Ensuring your turbocharged engine remains in peak condition is crucial. A faulty turbo can cause low oil pressure, leading to severe engine damage. By understanding the signs and taking proactive measures, you can protect your engine and extend its lifespan.
Key Takeaways
- Monitor oil pressure regularly: Always keep an eye on your vehicle’s oil pressure gauge.
- Listen for unusual sounds: Strange noises from the engine could indicate a turbo problem.
- Check for oil leaks: Oil leaks around the turbo area need immediate attention.
- Perform regular maintenance: Regular oil changes and inspections are essential.
- Use quality oil: High-quality oil helps maintain proper lubrication and pressure.
Future Outlook
The automotive industry is evolving rapidly. Turbocharged engines are becoming more efficient and reliable. Innovations in turbo technology are reducing the risks of low oil pressure. Advancements in engine monitoring systems provide real-time data to prevent issues before they escalate.
| Aspect | Future Improvements |
|---|---|
| Engine Monitoring | Real-time diagnostics and alerts |
| Turbo Technology | More efficient and durable turbos |
| Oil Quality | Enhanced formulations for better performance |
By staying informed and vigilant, you can ensure your turbocharged engine runs smoothly. The future looks promising with continuous advancements in technology.
Credit: www.hks-power.co.jp
Can Low Oil Pressure Cause Turbo Failure?
Yes, low oil pressure can cause turbo failure. Insufficient lubrication leads to overheating and damage. Regular oil checks are crucial.
What Are The Three Most Common Reasons For Low Oil Pressure?
The three most common reasons for low oil pressure are worn engine bearings, a failing oil pump, and low oil levels.
Can A Bad Turbo Cause Oil Loss?
Yes, a bad turbo can cause oil loss. Damaged seals or bearings can lead to oil leaking into the exhaust.
What Is The Oil Pressure For A Turbo?
The ideal oil pressure for a turbo typically ranges from 40 to 60 PSI. This ensures optimal performance and longevity.
Conclusion
A bad turbo can indeed cause low oil pressure. Regular maintenance is key to preventing such issues. Always monitor your vehicle’s performance. Address any signs of turbo failure promptly. Keeping your engine’s health in check ensures a smoother ride and longevity.
Stay proactive, and your car will thank you.



